
Periodic updates from the Election Integrity Partnership.

Missteps, Mistakes, and Misinformation About Maricopa County
The EIP analyzes the different narratives that emerged around the midterm elections in Arizona and explores the spread of both conspiratorial and authoritative information about voting issues.
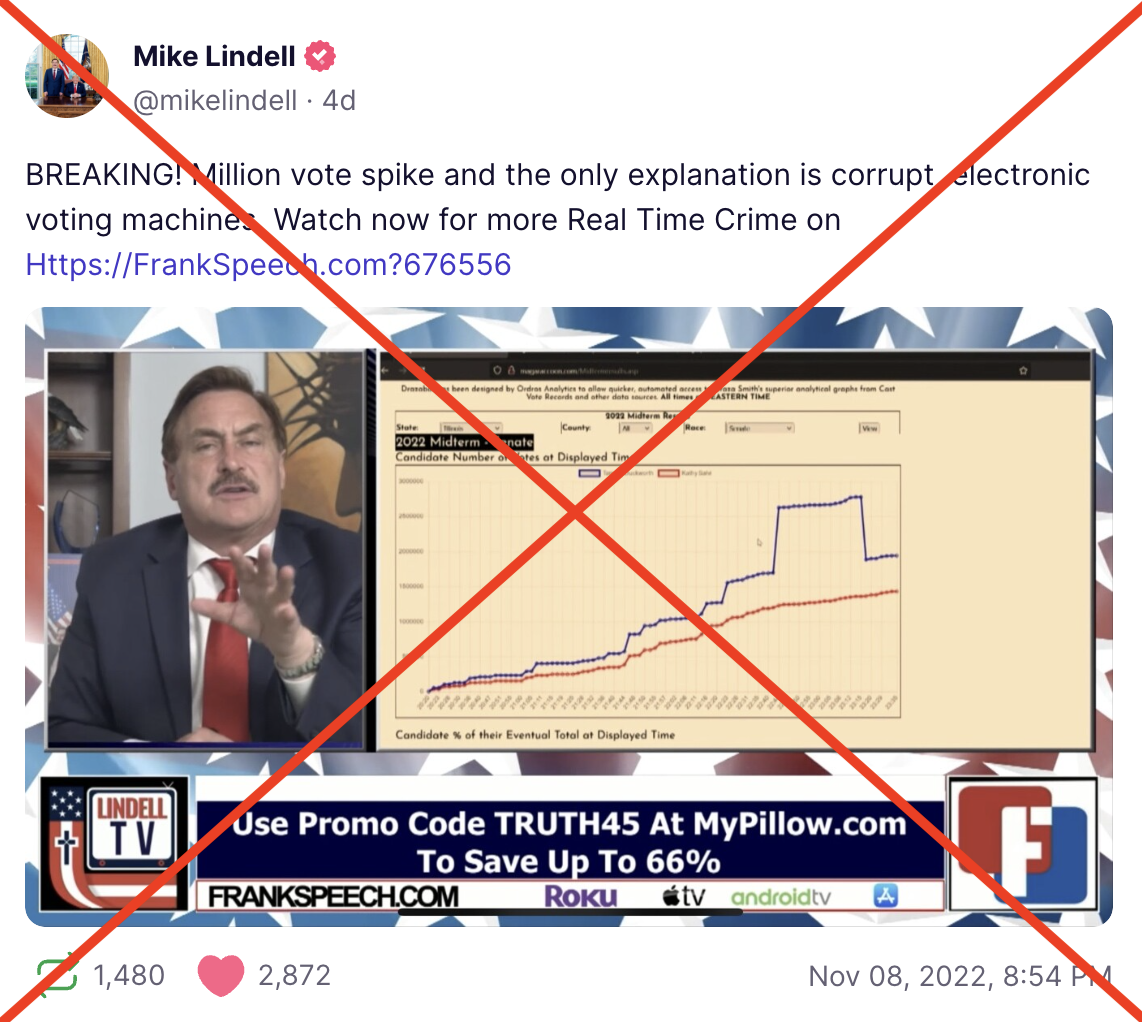
How Real-Time Visualizations of Vote Count ‘Spikes’ Can Lead to Unfounded Allegations of Election Fraud
Although vote count “spikes” have specific explanations and are not indicative of voter fraud, they have been incorporated into voter fraud allegations and conspiracy theories in prior elections and now in 2022.

Misinformed Monitors: How Conspiracy Theories Surrounding “Ballot Mules” Led to Accusations of Voter Intimidation
The EIP explores online conversation on Twitter and alt-platforms Truth Social and Telegram related to the monitoring of ballot drop boxes.
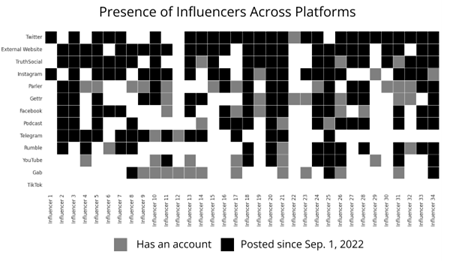
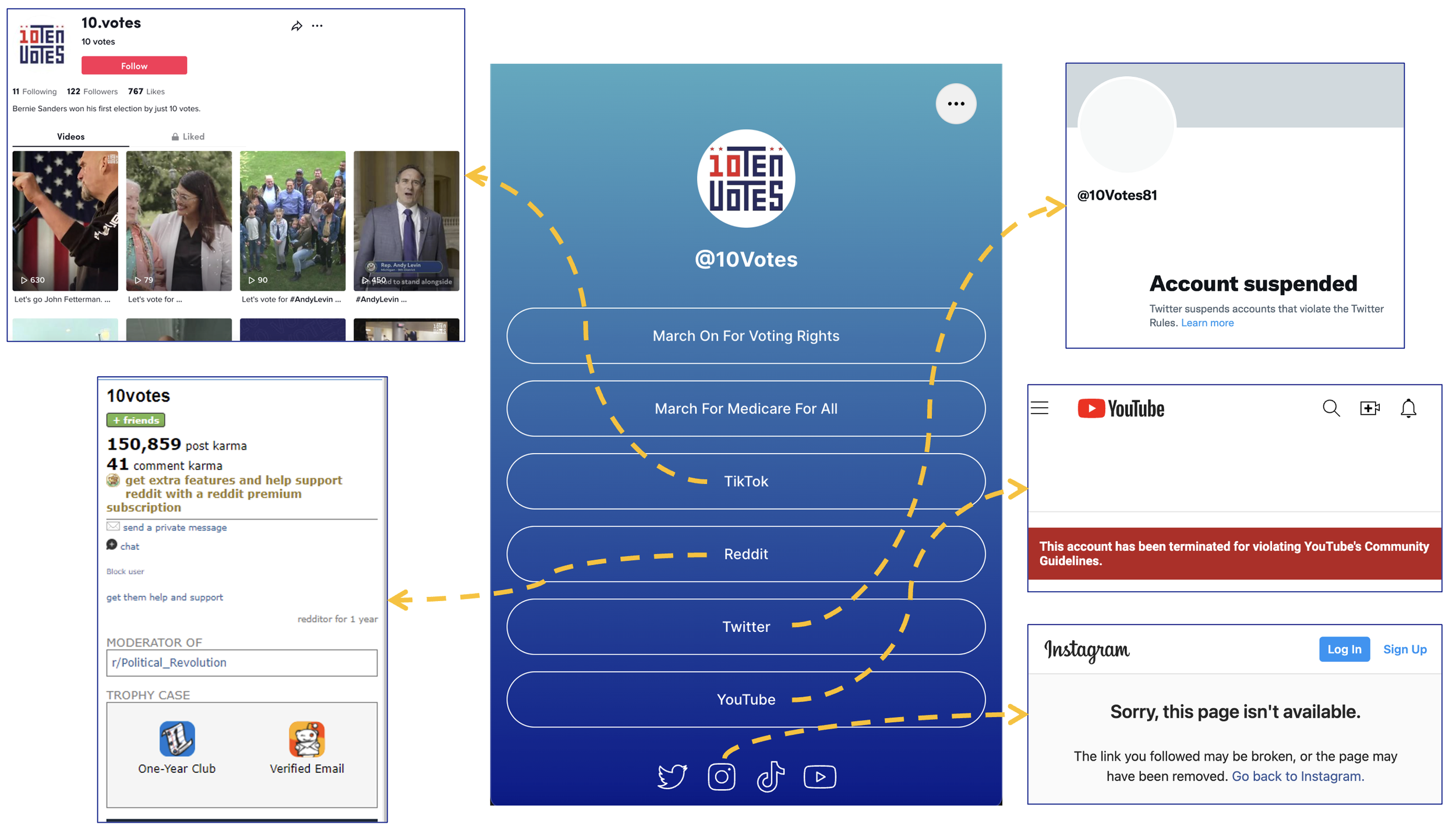
Beyond Twitter: The Election 2022 Social Media Ecosystem
We find that most of the voter fraud influencers from 2020 are still active on social media today, and that their online participation in 2022 spans a wide range of social media platforms.

Rumors, Conspiracy Theories, and Unsubstantiated Claims About Voting: What to Expect on and After Election Day 2022
We look back on some of our “What to Expect” predictions from the 2020 election, as well as new voting-related narratives we anticipate to take shape heading into Election Day 2022 and after.
Assessing Inauthentic Networks Commenting on the US Midterms
An assessment of five inauthentic networks on Twitter reveals techniques used by foreign actors targeting domestic US political discourse in the leadup to the 2022 midterm elections. The networks within the dataset were taken down under Twitter’s Platform Manipulation and Spam Policy. In this post, analysts from the Digital Forensic Research Lab and the Stanford Internet Observatory examine the content and tactics of the networks and their activity related to the US midterms. While some of the content posted by these networks and discussed in this blog post would not typically be in scope for the Election Integrity Partnership, commentary alleging election theft and fraud met our threshold for analysis, and we included the broader activity of these inauthentic accounts in this analysis.
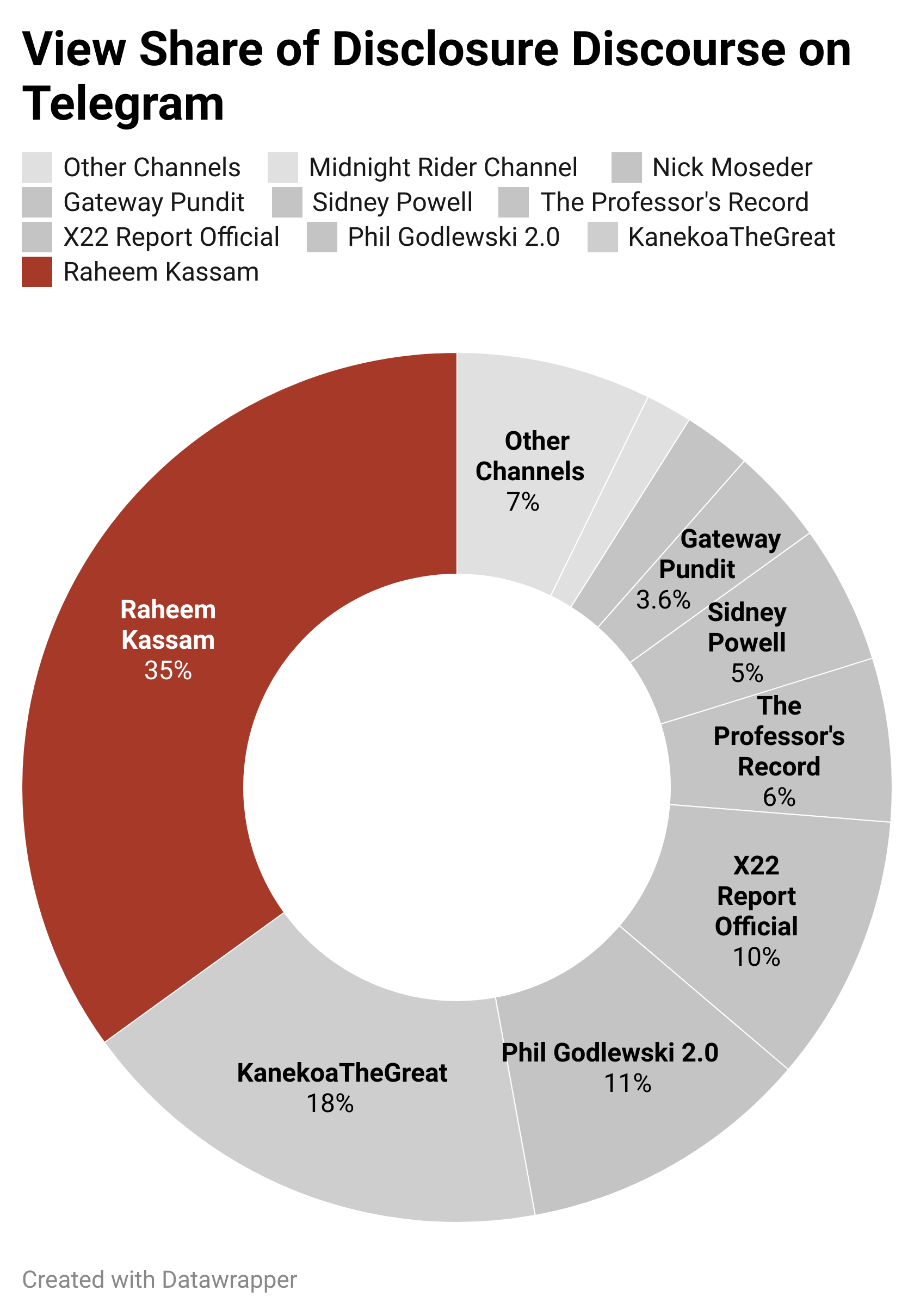
Election Vulnerability Disclosure Becomes Fodder for Dueling Conspiratorial Narratives on Telegram
The EIP analyzes the spread of associated narratives across multiple platforms, including Twitter and Telegram.

Platform Policy Analysis 2022
The Election Integrity Partnership assesses to what extent social media platforms have implemented or changed their election policies, both in terms of their scope and their enforcement.

Implying Intentionality: Understanding Unsubstantiated Allegations Around Election Administration Mistakes
We look at two case studies, in Colorado and Arizona, where unsubstantiated allegations of intentionality around mistakes or errors in election administration have spread rapidly online.

Confusion Over Election Technology Contributes to Rumors and False Claims
The Election Integrity Partnership examines the discourse associated with a recent incident in Kent County, Michigan, in which a poll worker was arrested for allegedly tampering with an electronic poll book. While the technology breached has no connection to election results, online the breach was interpreted as an instance of election fraud or cheating.

The DeJoy Case: Criticism of Poor Performance, Rumors of ‘Sabotage’
Online narratives about U.S. Postmaster General Louis DeJoy and the U.S. Postal Service underscore the challenge of disentangling legitimate criticism from rumor and conspiracy theorizing.

Voting Rights Legislation Framed to Support Election Conspiracy Theories About Non-citizens Voting
Election Integrity Partnership (EIP) researchers examined online discourse around two situations earlier this year — New York City’s law allowing non-citizens to vote in local elections and the U.S. Department of Justice’s challenge of an Arizona state law — to gauge the current level and nature of non-citizen voting conspiracism in current election discourse.


10 Factors That Shape a Rumor’s Capacity for Online Virality
Election Integrity Partnership researchers share a threat framework adapted for election officials, analysts, and crisis communication teams.

The Election Integrity Partnership in 2022: Our Work Ahead
In the 2020 U.S. elections, false and misleading online information gave rise to physical and legal challenges to the certification of the election’s results. In 2022, we will once again face such challenges. In the primaries this year, we have already witnessed the recurrence of spurious claims from the 2020 election.
